|
If you find this helpful, please click the Google |

The <datalist> Tag in HTML 5
The <datalist> tag is used to create a combo box input field with autocomplete in an HTML form. Suggestions for autocompletion come from predefined options coded with the <option> tag.
This is an actual working example of the <datalist> tag example code below. If your browser supports the <datalist> tag, the <option value>s will be displayed after you start typing data into the input field, then it should appear something like this:
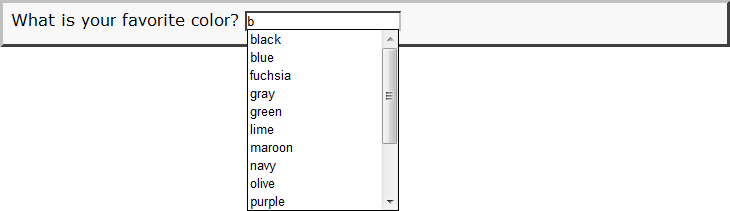
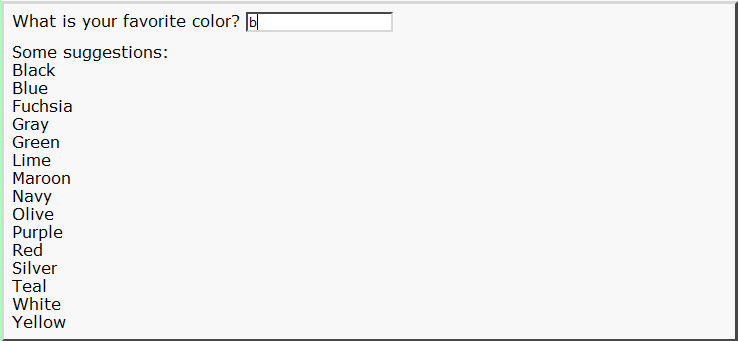
If your browser does not support the <datalist> tag, the options will always be displayed, even before starting to type data into the input field, possibly like this:

... or maybe like this:
<datalist> Tag Syntax
<body> ... ... phrasing content expected ... <datalist id="..."> <option value="..." label="...">... text content ...</option> ... phrasing content ... </datalist>... ... </body>
Rules for coding HTML datalist elements
Make sure you understand the difference between a tag and element and are familiar with the definitions of namespace and other HTML terms.
- Code the datalist element where phrasing content is expected.
- Begin the datalist element with a starting <datalist> tag. The element name uses lower case letters and should be in the HTML namespace, which it will pick up automatically from the
xmlnsattribute on the <html> tag. - Inside the <datalist> starting tag, include an id attribute that can be used to refer to the data list.
- Inside the datalist element, between the starting
<datalist>tag and the ending</datalist>tag, code the option elements for the predefined suggestions. - Also inside the datalist element,code the fallback text and/or phrasing content.
- End the datalist element with a matching
</datalist>closing tag.
datalist Content Model
Content of the datalist element
The content of the datalist element consists of a list of option elements along with fallback content for browsers that do not support the <datalist> tag.
Note that the options cannot be grouped with the <optgroup> tag like the options in a <select> list can.
According to the HTML 5 specifications:
In the rendering, the datalist element represents nothing and it, along with its children, should be hidden.
However, this applies only to browsers that support the <datalist> tag. Browsers that do not support <datalist> will display the content of the datalist element, including the text content of any child option elements. See the examples of the <datalist> tag below for how to hande this.
<datalist> Tag Attributes
Attributes of the <datalist> tag
| global attributes | In addition to the personal attributes of the <datalist> tag below, any of the common HTML attributes can also be coded. |
| id | id global attribute
The id attribute is used to associate the data list with an input element via the <input list> attribute. |
<datalist> Tag Examples
Examples of the datalist tag in HTML 5
Example of <datalist> with inline list values
(see <datalist> tag demo above)
<label>What is your favorite color? <input name="color" type="text" list="html-colors"/>
<datalist id="html-colors"><br/>Some suggestions:
<option value="black">Black</option>
<option value="blue">Blue</option>
<option value="fuchsia">Fuchsia</option>
<option value="gray">Gray</option>
<option value="green">Green</option>
<option value="lime">Lime</option>
<option value="maroon">Maroon</option>
<option value="navy">Navy</option>
<option value="olive">Olive</option>
<option value="purple">Purple</option>
<option value="red">Red</option>
<option value="silver">Silver</option>
<option value="teal">Teal</option>
<option value="white">White</option>
<option value="yellow">Yellow</option>
</datalist>
</label>
Example of <datalist> with <option label>s
<input name="datalist-item" list="datalist-items" size="40" style="border: 1px solid black" /> <datalist id="datalist-items"><br/>Some suggestions: <option value="datalist item without label"></option> <option value="datalist item with label" label="label for datalist item"></option> <option value="datalist item with text">text for datalist item</option> </datalist>
In browsers that do not support the <datalist> tag, the text content of any <option> tags ("text for datalist item" above) appears along with any other fallback code. The <p>Some suggestions:</p> is included to indicate to the user what the fallback text from the <option>s means.
Here is an actual working demo of the code above. (Do View Source to verify that this page is using the HTML 5 DOCTYPE. You can also verify it is Valid HTML 5 using the HTML Validator.)
Note: The first browser where this datalist demo actually works is Opera. It may not work yet in other browsers.
Changes in HTML 5 - <datalist> Tag
What's new in HTML 5
Differences between HTML 5 and earlier versions of HTML
The <datalist> tag did not exist in older versions of HTML.
The 2000-2010 Recommendations from the W3C HTML Working Group defined the HTML namespace for the names of all HTML element types, which now includes the element name. In older (pre-2000) versions of HTML, element type names were not associated with a namespace.