|
If you find this helpful, please click the Google |

The <option> Tag in HTML 5
The <option> tag is used to create an item in a drop-down box in an HTML form.
This is an actual working example of the <option> tag example code below.
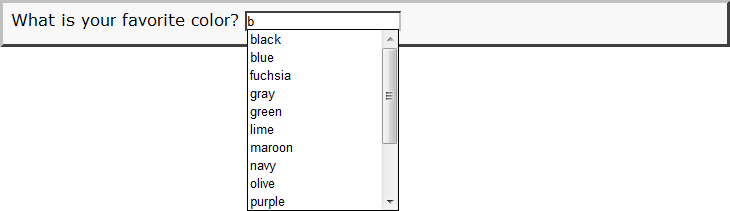
One alternative, for an autocomplete dropdown, uses an <input> tag that references a <datalist> tag instead:
<option> Tag Syntax
Rules for coding HTML option elements
<body> ... flow content expected ... <form method="POST" action="form-handler"> ... flow content ... <select> ... <option value="...">...</option> ... </select> ... flow content ... </form> ... </body>
Rules for coding the HTML option element
Make sure you understand the difference between a tag and element and are familiar with the definitions of namespace and other HTML terms.
- Inside a select element, include an option element for each option in the select list.
- Begin the option element with a starting <option> tag. The element name uses lower case letters and should be in the HTML namespace, which it will pick up automatically from the
xmlnsattribute on the <html> tag. - Inside the <option> tag, code a value attribute with the value of the field that is to be sent to the destination specified in the <form action> attribute.
- Inside the option element, between the starting
<option>tag and the ending</option>tag, code the text content of the option. - End the option element with a matching
</option>closing tag.
<option> Content Model
Content of the option element
The content of the option element can include HTML comments and text content. It should not have any child elements.
<option> Tag Attributes
Attributes of the <option> tag
| global attributes | In addition to the personal attributes of the <option> tag below, any of the common HTML attributes can also be coded. |
disabled="disabled" |
Sets the value of the <option disabled> boolean attribute to true. Omitting it sets to false. |
label |
|
selected="selected" |
Sets the value of the <option selected> boolean attribute to true. Omitting it sets to false. |
value |
<option> Tag Examples
Examples of the option tag in HTML 5
Example of <option> tags under an HTML <select> tag for options in an HTML drop-down box
(see <option> tag demo above)
<form method="POST" action="development-language.cgi">
<label>Language:</label>
<select name="language">
<option value="">Select a language ...</option>
<option value="cpp-c-sharp">C++ / C#</option>
<option value="html">HTML</option>
<option value="java">Java</option>
<option value="javascript">JavaScript</option>
<option value="objective-c">Objective-C</option>
<option value="perl">Perl</option>
<option value="php">PHP</option>
<option value="ruby-on-rails">Ruby on Rails</option>
</select>
</form>
Example of <option> tags for options in a <datalist>
<form method="post" action="">
<input name="datalist-item" list="datalist-items" size="40"
style="border: 1px solid black"
/>
<datalist id="datalist-items">
<p>Your browser does not support the HTML 5 <datalist> tag yet.<br/>
(This is the fallback code - you should only see one text item below.)
</p>
<option value="datalist item without label"/>
<option value="datalist item with label" label="label for datalist item"/>
<option value="datalist item with text">text for datalist item</option>
<optgroup label="Grouped items">
<option value="optgroup item without label"/>
<option value="optgroup item with label" label="label for optgroup item"/>
</optgroup>
</datalist>
</form>
In browsers that do not support the <datalist> tag, the text content of any <option> tags ("text for datalist item" above) appears along with any other fallback code. Therefore, it is better to use the label attribute for the label instead.
Changes in HTML 5 - <option> Tag
What's new in HTML 5
Differences between HTML 5 and earlier versions of HTML
The 2000-2010 Recommendations from the W3C HTML Working Group defined the HTML namespace for the option element type name along with the names of all HTML element types. In older (pre-2000) versions of HTML, element type names were not associated with a namespace.